AI Drug Discovery Technology Platform
Ninnion’s exclusive AI drug discovery platform partnership, is exclusive for creating next generation psychedelics which are New Chemical Entities for treating brain injury, inflammation, chronic pain and addiction In the next 5 years, Ninnion will create 10 or more novel, next generation psychedelic drug candidates with optimized pharmacological profiles, improved tolerability and safety. Because of the high unmet need in these areas, we will be well positioned to leverage FDA expedited regulatory pathways including breakthrough therapy, fast track, and orphan designations tolerability and safety. Because of the high unmet need in these areas, we will be well positioned to leverage FDA expedited regulatory pathways including breakthrough therapy, fast track, and orphan designations.


Partnership
Cyclica
Cyclica Inc. is our partner for data-driven drug discovery as they advance molecules that address the complex conditions that we treat. They use a unique computational approach to pharmacology through a proteome-wide lens in order to evaluate multiple target drug interactions.
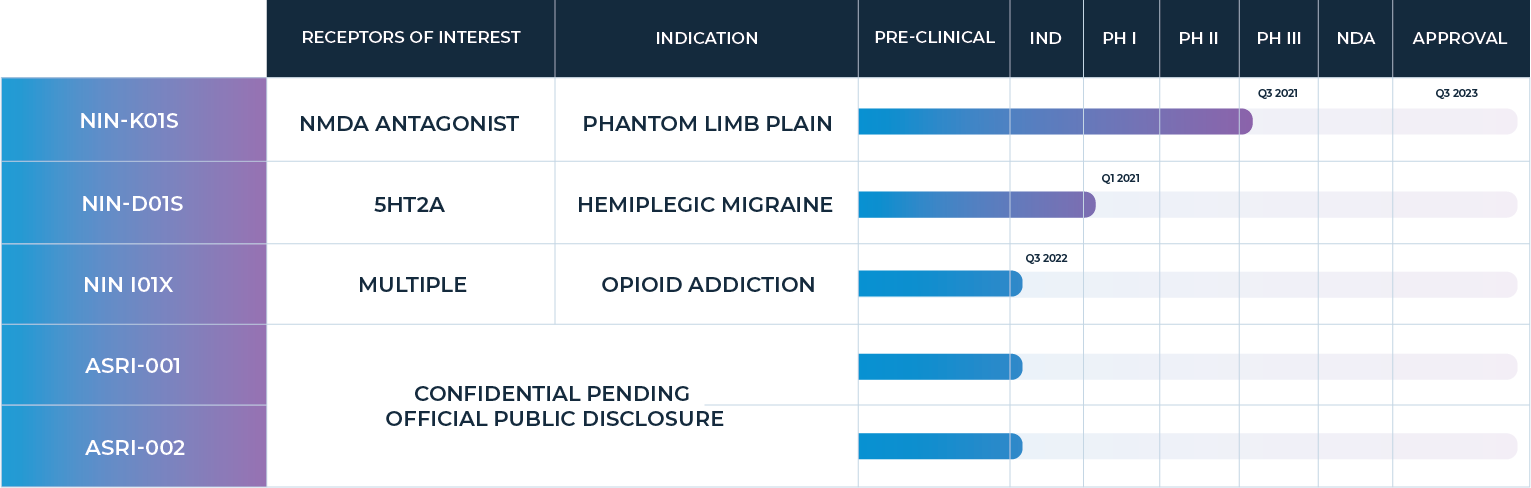
Development Pipeline
NIN-S119 Ischemic Stroke Recovery:
Stroke is a leading cause of death and serious disability for adults. According to the CDC, approximately 800,000 people in the United States have a stroke each year, and ~23% of these patients will experience a 2nd stroke. An Ischemic stroke occurs when the flow of blood supply to part of the brain is blocked, preventing brain tissue from getting oxygen and nutrients. Brain cells begin to die just minutes after such a blockage occurs. If the patient makes it to the emergency room within three hours from the onset of symptoms of an ischemic stroke, they are eligible to receive fibrinolytic therapy such as Activase, which works to break up the clot(s) causing the stroke and hopefully limiting the damage to brain tissue.
Unfortunately there is a lack of awareness around the symptoms of a stroke and many patients delay seeing a doctor until it’s too late. In fact only about 10% of stroke patients are able to be treated with Activase because they did not arrive at the hospital within the three hour window from the onset of symptoms required for administration of this often life-saving drug.
When a patient suffers a stroke, the affected part of the brain dies, so rehabilitation exercises focus on re-training and strengthening the remaining brain cells which learn to perform these functions. Standard rehabilitation protocols for patients include occupational, speech, and physical therapy to overcome functional deficits.
Overcoming functional deficits can take months of rehabilitation and rely heavily on neuroplastic processes to retrain a new part of the brain to restore lost function. Only about 10% of patients make a complete recovery, 25% recover with minor deficits, 40% experience mild to severe deficits and 10% require long-term specialty care
Currently, there are no approved drug therapies for patients recovering from stroke.
Ninnion has begun development of NIN-S119, our proprietary, short-acting substituted tryptamine to treat patients recovering from ischemic stroke. NIN-S119 will be used in conjunction with physical/occupational therapy to potentiate the ability to form new neuronal connections (synapses) and strengthen the connectivity of remaining brain cells engaged during therapy. The ability of the brain to make physical and functional changes is called neuroplasticity.
Neuroplasticity is produced through the processes of neurogenesis (the generation of new brain cells) and synaptogenesis (the formation of new functional connections between brain cells).
NIN-S119 is postulated to enhance stroke recovery through inducing neuroplasticity. This means it induces the formation of new connections between nerve cells, in essence “re-wiring” the brain. Such brain “re-wiring” could prove beneficial for stroke recovery by creating new brain circuitry that could restore function to brain areas damaged by stroke.
NIN-S119 produces its neuroplastic effects by stimulating the serotonin 2A (5-HT2A) receptor. Numerous studies have shown that psychedelic drugs that stimulate the 5-HT2A receptor not only dramatically increase synaptogenesis, but also stimulate neurogenic activity, resulting in increased connectivity between brain cells and the growth of new brain cells.
Stimulation of the 5-HT2A receptor leads to activation of biochemical processes leading to the synthesis and release of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF). BDNF is a natural growth factor that stimulates neurogenesis and synaptogenesis. In this manner, NIN-S119 stimulates the brain’s innate ability to heal.
While drugs that produce serotonin 2A receptor agonism can induce “psychedelic” mental states (e.g. LSD, mescaline, DMT, etc.), the doses required to stimulate neuroplasticity are much lower than those required to produce “psychedelic” effects, potentially enabling the use of NIN-S119 in stroke recovery without these psychedelic effects. The lack of psychedelic effects would make NIN-S119 much easier to use clinically, reducing the time and effort of clinical staff, opening the potential for administration by the patient at home.
NIN-S119 would be the first drug of its kind in the treatment of stroke, potentially making it eligible for Breakthrough Therapy designation by the FDA, a designation that can accelerate the development timeline. IND-enabling toxicology will be completed and initial clinical trials initiated in 1Q23.